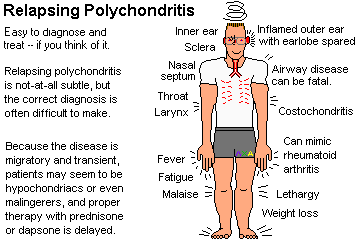
Relapsing polychondritis causes sudden pain
in the inflamed tissue at the onset of the disease. Common symptoms are pain,
redness, swelling, and tenderness in one or both ears, the nose, throat,
joints, and/or eyes. The lobe of the ear is not involved. Fever, fatigue, and
weight loss often develop.
Ear and nose
Inflammation of the ears and nose can cause
deformity (saddle nose deformity and floppy ears) from weakened cartilage.
Impaired hearing, balance, and nausea can be caused by inner ear inflammation.
Respiratory tract
Inflammation of the windpipe or trachea can
lead to throat pain, hoarseness, and breathing difficulty. This is a
potentially dangerous area of inflammation in patients with relapsing
polychondritis and can require assisted breathing methods when severe.
Joints
Joint inflammation (arthritis) can cause
pain, swelling, and stiffness of the joints, including of the hands, knees,
ankles, wrists, and feet.
Eye
Eye inflammation can be mild or severe and
can damage vision. Cataracts can be caused by the inflammation or from the
cortisone used to treat relapsing polychondritis (see below).
Other
Other tissues that can develop inflammation
include the aorta (which can lead to aneurysm or aortic valve weakness),
tissues in or around the heart (myocarditis and pericarditis), the skin
(vasculitis), and the nerves from the brain (cranial nerve palsies).